Cannabinoids are chemicals found in cannabis that offer a surprisingly wide array of therapeutic benefits. They are produced in the resin glands of the plant, or trichomes, and get stored in those frosty-looking crystals found on the flower.
Scientists have identified 113 different cannabinoids that can be found in cannabis, and those are just the ones we know about. We’ll likely discover new cannabinoids in the future.
The Endocannabinoid System
We have a few different types of receptors in our body that bind to cannabinoids. The two we know the most about are the CB1 and CB2 receptors.
The CB1 receptor is mostly in the brain but is also found in different organs and glands, which leads to far-ranging effects on hormones and bodily systems.
The CB2 receptor is found throughout the body, primarily in the immune system and also the bones.
The different effects specific cannabinoids have on these, and other receptors, lead to the unique experiences and uses of different strains.
The Entourage Effect
Think of this like chemical teamwork.
Beyond the 113 identified cannabinoids, there are also 200+ terpenes and dozens of other less-understood compounds within cannabis.
Think about that.
In a single puff, you are getting an entire cocktail of biochemically active molecules.
The genius of cannabis’ biochemistry is that they all work astoundingly well together. These chemicals work in harmony, complementing, shading, and balancing the effects of the plant as a whole.
The overall effect of all of this put together is known as the “Entourage Effect.” It is the entire spread of all the different compounds that come with cannabis working together to create the overall effect. Not just THC or CBD.
So now that we have an understanding of the whole picture, let’s look at some of these chemicals individually.
The 6 Most Common Cannabinoids
THC
This most (in)famous of all the cannabinoids is highly psychoactive and binds CB1 receptors in the brain. Because it is so potent, humans have selectively bred for it, and most strains you find now will contain extremely high percentages of THC. It is known for its pleasant euphoria and is a cannabinoid treatment for nausea, stress disorders, and anxiety.
CBD
Gaining in popularity, cannabidiol primarily binds CB2 receptors in the body and is non-psychoactive, creating tremendous potential for medical use without impairing cognitive function. It is a potent anti-inflammatory and has an overall calming effect on the body. This cannabinoid treatment profile lowers blood sugar, can help manage seizures, and treat chronic pain, to name just a few of its benefits
CBC
This third most abundant cannabinoid shows promise as a cannabinoid treatment for cancer and may be the active compound behind anecdotal stories of people claiming to have “cured” — or reversed — cancer with cannabis oil.
CBG
Beyond its effects on CB receptors, this cannabinoid also regulates the amino acid GABA, which is involved with mental stability and other neurological functions.
CBN
Rarely found in raw cannabis, CBN is created in the curing process of drying the flower. CBN is responsible for the “stoned” effect. It is highly sedative, stimulates appetite, and leads to an aptly named side-effect known as “couch lock.”
THCA/CBDA
These are raw forms of CBD and THC that are chemically altered by heat. This cannabinoid treatment has been proven to be useful as a potent anti-inflammatory, and some claim raw cannabis as a superfood. Cannabis salad, anyone?
The world of cannabis chemistry is in its infancy, but in the future, we can expect a whole new menu of cannabis cultivation oriented around specific cannabinoid treatment profiles!
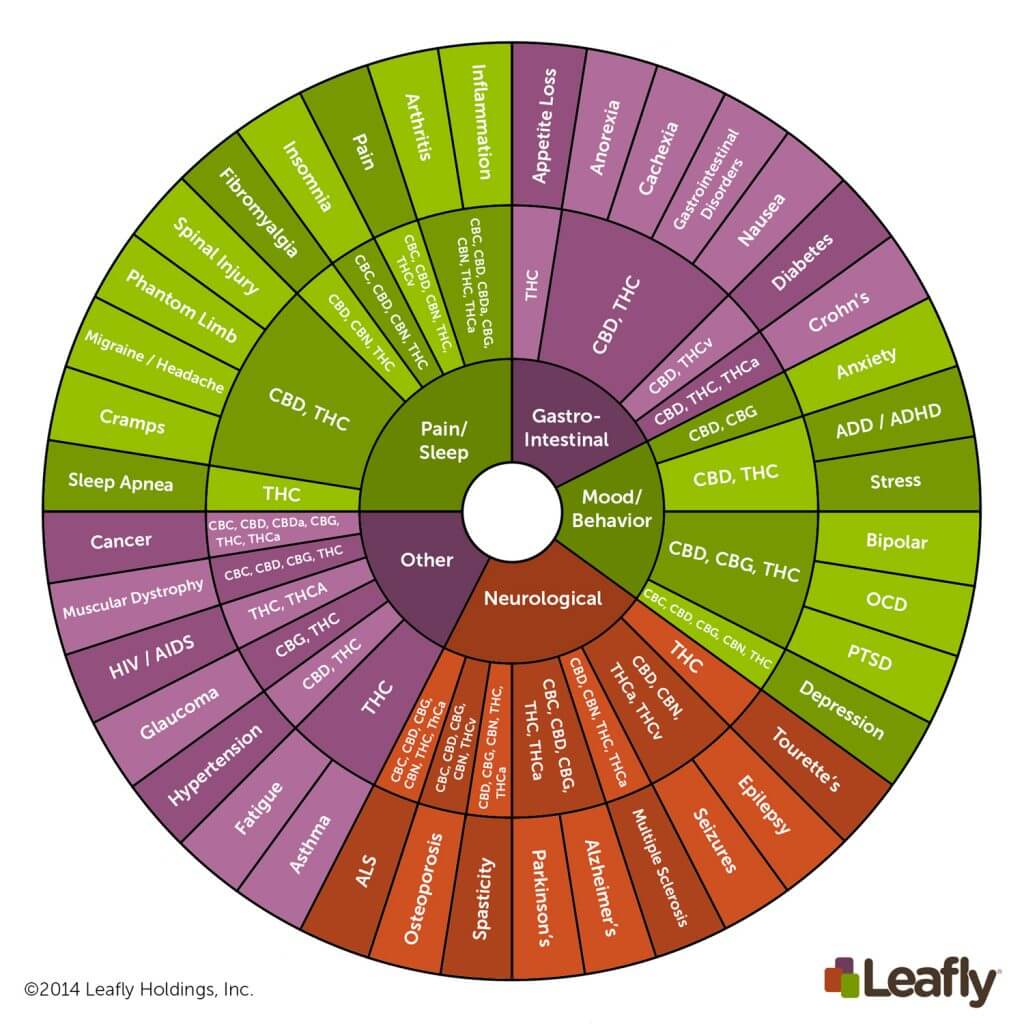
For a complete look at the terrain of cannabinoids, explore this infographic from Leafly: